Looking for a GMP audit checklist? You’re in the right place. Whether in Canada, the US, the UK, or another country, there are strict pharmaceutical manufacturing regulations and requirements. Utilizing a GMP Audit Checklist is one tool many pharmaceutical manufacturing companies use to maintain regulatory compliance.
What is a GMP Audit?
A GMP Audit or Good Manufacturing Process Audit is an inspection of a manufacturing facility and practices where appropriate controls are required. GMP regulations date back to April of 1969, published in the CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) in the United States. Since then, many other countries like Canada and the United Kingdom have solidified similar regulations. (source)
Good Manufacturing Practices, also known as current Good Manufacturing Practice’, or cGMP) was also established by the WHO to monitor and control the manufacturing standards of globally traded pharmaceutical products. The adoption of GMP regulations occurred initially in 1968, with a recommendation by the World Health Assembly for best GMP practices coming forward in 1969. (source)
In 1991 the WHO released a supplementary annex regarding the manufacture of biological products and best GMP practices. These products are vaccines, blood products, cell therapies, and other biologically based manufactured treatments.
Given the sensitive nature of manufacturing pharmaceutical products, we can assume that a GMP audit about pharmaceuticals is a thorough inspection and reporting process involving the regulatory Good Manufacturing Practices set forth by the government (or WHO) of the facility in question. To simplify, it’s a check to see if the pharmaceutical manufacturer is following current rules and regulations for safe product manufacturing.
The GMP Audit Checklist template we’ve created focuses on the WHO GMP requirements.
Included In The GMP Audit Checklist
A GMP plan should include the following (at a minimum):
- Define and control manufacturing processes
- Critical process validation
- Validation as per specifications
- Control batch manufacturing records
- Changes to the process must face an evaluation
- Changes that affect the quality of the product must meet validation
- You must write procedures in clear and concise language
- Team members must be trained in production, quality control, and observational documentation.
- Documentation of quality control during the final stages of production is essential. This documentation must include validation of all previous GMP steps and practices.
- Deviation from procedure must be documented and investigated.
- You must maintain documentation for the life cycle of the batch and for any time past stipulated by regulations within your country.
- You must maintain a well-defined recalling procedure.
- It would be best if you seriously investigated product complaints to determine defects’ root cause and effects. It would be best if you took appropriate corrective action.
Let’s dive deeper into our template and go over the basics so you and your team are well prepared.
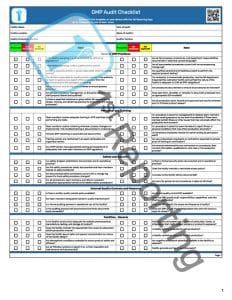
The GMP Audit Checklist is geared towards pharmaceutical applications but could find use in most manufacturing industries. The template is comprised of three pages. Here’s a breakdown of each and the subsequent sections in each.
GMP Audit Checklist Page One
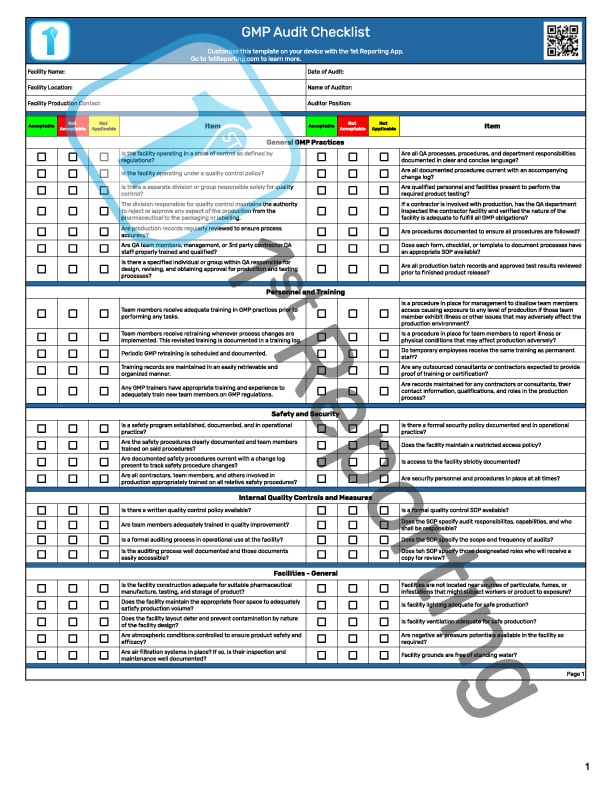
- Administration – An area where the facility name, location, the auditor name, audit date, facility contact, and auditor position information are all recorded.
- General GMP Practices – We begin the audit with some more general GMP queries. This section includes a focus on general quality standards compliance concerns. Similarly, there are questions about the quality control unit to facilitate quality assurance and control procedures. The section includes some basics of production records, questions concerning authorized personnel, and appropriate conditions for documenting work practices and observations.
- Personnel and Training – A critical aspect of the GMP auditing process is determining proper personnel training. Noting points about using qualified personnel is essential to include in the GMP compliance procedures. Training to avoid safety hazards and impactful production processes affecting product quality is vital to pharma. Therefore, it is included in GMP best practices to utilize the utmost training, not just great written instructions, but actual training to avoid GMP non-compliance.
- Safety and Security – Pharmaceutical manufacturing is strictly regulated, and intensive safety and security measures are paramount. This section of the GMP audit template covers these safety and security issues. Security isn’t merely in place to keep personnel and employees from accessing the incorrect facility controls. Security is about maintaining a sanitary condition for production and preventing contamination from deliberate outside sources who would see people injured. Pharmaceuticals are a massive industry, and industrial espionage is a severe and genuine concern here, so security is paramount for several reasons.
- Internal Quality Control and Measures – Internal quality controls are essential to a robust pharmaceutical manufacturing process. Implementing controls is easy following this section of the audit template. Drug manufacturers need strong laboratory controls on quality and measurement. Quality assurance is paramount to in-process materials, raw materials, and the entire supply chain. In fact, it needs consistent quality. The only way to achieve this is via stringent internal quality control measures.
- Facilities – General – The general facilities questions relative to GMP are found in this segment of the audit template. The general facilities section is mainly concerned with facility layout (set up to prevent contamination), a suitable floor space, no standing water on the grounds, and appropriate atmospheric controls to suit the production and storage of pharma products.
GMP Audit Checklist Page Two
- Facilities Maintenance and Sanitization – Maintaining sanitary operations is a prerequisite of the GMP regulation regarding pharmaceutical and drug product manufacturing. The finished products must be free of contamination, and the only way to achieve this is by using a robust cleaning procedure using sanitizing agents. Similar to a food product, you wouldn’t want pharmaceuticals facing contamination in any aspect of their production processes, from material or component production to distribution.
- Facility Equipment – Equipment cleaning and maintenance are required for all equipment that comes into contact with the product or packaging. Your quality control unit must ensure the safety and cleanliness of all equipment. Proper equipment training is essential for all equipment, especially for cleaning equipment that may contact the product. Similarly, lubricants and cleaners can give anything from raw materials to the finished drug product contamination. Therefore, we are also concerned with equipment liquids and other items that accompany the use and maintenance of said equipment.
- Materials Controls – Raw materials, components, and even packaging materials are strictly controlled in a robust GMP environment where drug products are manufactured. The GMP checklist includes several questions concerning materials controls required in a GMP inspection of facilities and production.
GMP Audit Checklist Page Three
- General Operations – General operations are observed on the GMP checklist. This section covers many other topics sometimes missed on other GMP audit checklists – but not ours! We cover issues from product quality and yield calculations to testing procedures for drug products. The GMP checklist is concise and thorough, encompassing most of the processes necessary to host a robust GMP facility that drives valid results from GMP audits.
- Product Controls – The product controls section of the GMP checklist covers more product documentation, quality assurance via sample testing, and product deviation management.
- Complaint Handling – Complaint handling is a significant aspect of operational concern in the pharmaceutical industry. Complaints must face consistent and rigorous investigation procedures to ensure the product’s safety. Medical examinations or any other potential data is collected, and you must document the procedures for managing complaints and collecting pertinent data. This section of the audit checklist contains items dealing with complaints.
- Notes and Sign-Off – All audits worth their salt need a sign-off section where personnel sign to the validity of the results. The signature is the quality assurance of the writer that the person has received the appropriate training to complete the GMP audit procedures. Production GMP audits should also have a witness and potentially even a sign-off by higher authority personnel. The sign-off section has a place for both employees and management to determine the document’s completion and sign off on it.
Who Regulates GMP Practices In Pharmaceuticals?
Most countries carry their own regulations. For example, here are some references for three popular countries:
- Canada – Health Canada – Good Manufacturing Practices Guide For Drug Products (GUI-0001)
- United States of America – Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- United Kingdom – The Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
If you were to investigate the regulations for each country, you’d notice a lot of similarities between the countries. This fact is because most countries in the civilized world follow and recognize the international GMP requirements set forth by the WHO.
- World Health Organization – Good Manufacturing Practices brief
- World Health Organization – Good Manufacturing Practices for Biological Products, Annex 2, TRS No 999.822
Why is a GMP Audit Essential to the Pharmaceutical Industry?
There are five key reasons why you should consider performing internal GMP audits. It will help your organization prepare for government-enforced audits. Preparation is the best strategy for regulated industries, and the pharmaceutical industry is probably the most vital in that regard. Here are the five primary considerations for a GMP audit:
- To protect consumers’ health by detecting and preventing the distribution of defective products.
- To ensure quality and consistency in product manufacturing.
- To ensure that products are manufactured in a manner that meets regulatory requirements.
- To identify weaknesses in your Quality Management System (QMS).
- To maintain the reputation of the pharmaceutical industry.
If you want your organization to consistently achieve good results regarding the above five items, you’ll need to focus on a solid documentation policy.
Due to the essential nature of Good Manufacturing Practices in the pharmaceutical industry, it’s vital to maintain distribution records for the FDA (or other regulatory body) and maintain robust written procedures for your team.
There are several other actionable items that you can do to achieve the best results towards a perfect GMP environment. Let’s take a look.
How To Achieve GMP Superiority In Pharmaceutical Facilities
We know that achieving GMP superiority is a priority for your organization. We’ve put together these ten tips to help you and your team move forward toward the GMP winning circle to give you a boost.
- Ensure personnel gets properly trained in GMP guidelines and procedures. Promoting a robust training regiment within your organization ensures that your team is the most qualified in their fields.
- Implement quality control measures throughout manufacturing, from supply chain to finished product distribution.
- Perform regular internal GMP audits and address any discrepancies immediately.
- Utilize written procedures, even for the GMP audit itself, for maximum GMP compliance potential.
- Maintain cleanliness and safety in all facility areas, from the manufacturing floor to the office space.
- Enact proper security measures to protect your product, ingredients, and intellectual property.
- Keep detailed records of all aspects of the manufacturing process
- Investigate and address any complaints swiftly and effectively
- Use a GMP audit template like we’ve created here for you. Or, if you’d instead not print inspection documents, keep reading.
- Use a powerful tool like 1st Reporting. GMP compliance is much easier with a digital reporting app that you can use right on your mobile device. Inspections are much easier with a mobile reporting platform like 1st. It will make your inspection process easy, and you’ll wonder why you’ve never used this solution before. You can use 1st for everything from in-process inspections to daily equipment safety audits. No matter the audit type, the customizability of 1st ensures that you’ve got the tools you need from the supply chain to the sales floor.
By following these simple steps, you can comply with GMP guidelines and ensure that your products are of the highest quality. Don’t let your competitors get ahead of you – start implementing these changes today!