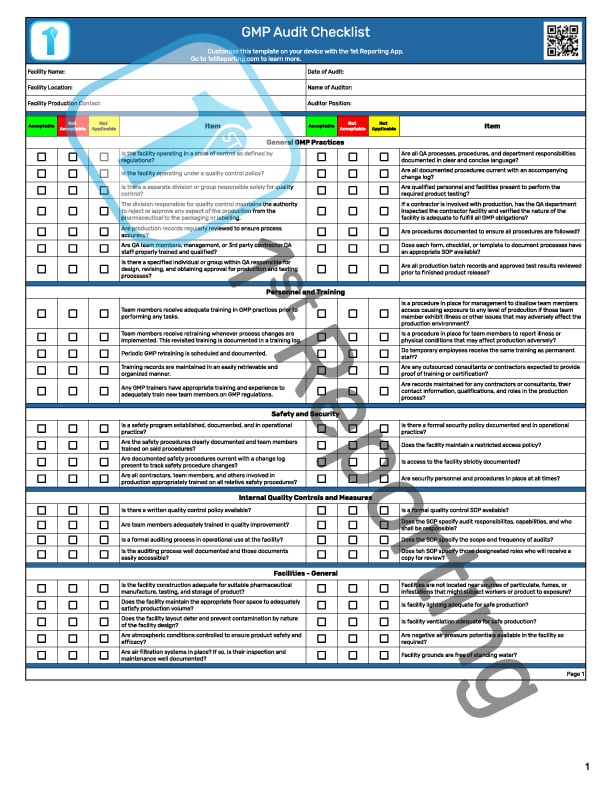
If you’re looking for a Food GMP Audit Checklist, you’re in the right place. We’ve got many downloadable templates you can use. Even better, we have an app for taking your documents digitally (no more printers? Tell me more!).
The Food GMP Audit Checklist template we provide here is free and downloadable. Furthermore, this article will serve as a guide you can use to help train your team members.
Don’t hesitate to bookmark this page, so you can easily share it later with your team. It will save you time and money in training if you use our free resources. So without further to-do, let’s dive in.
Included In The Food GMP Audit Checklist
Our Food Industry GMP Audit Checklist is based on the GMP practices 1.0 (July 2022) Official Government Use inspection checklist provided by the USDA, AMS, SCP, and Specialty Crops Inspection Division. We’ve compressed the official checklist to make it easier for your company. Still, all the essential information is there, so it’s reasonably comprehensive.
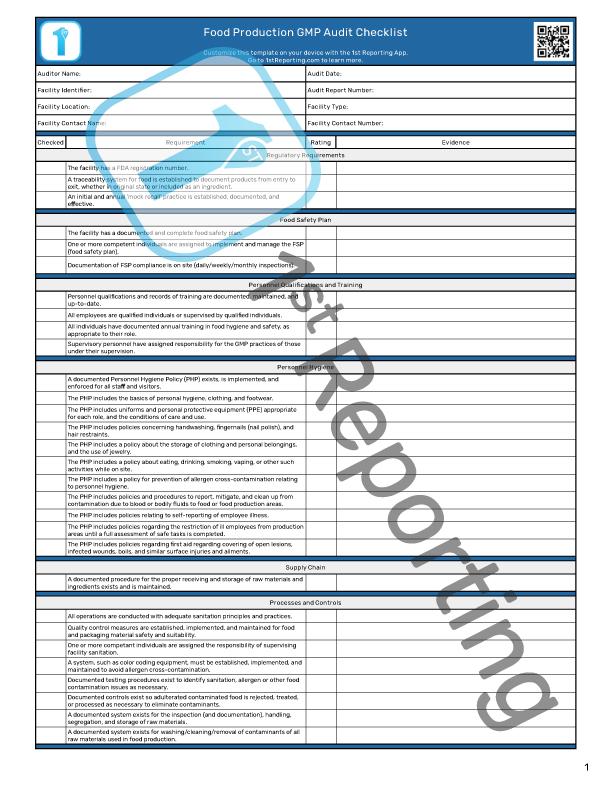
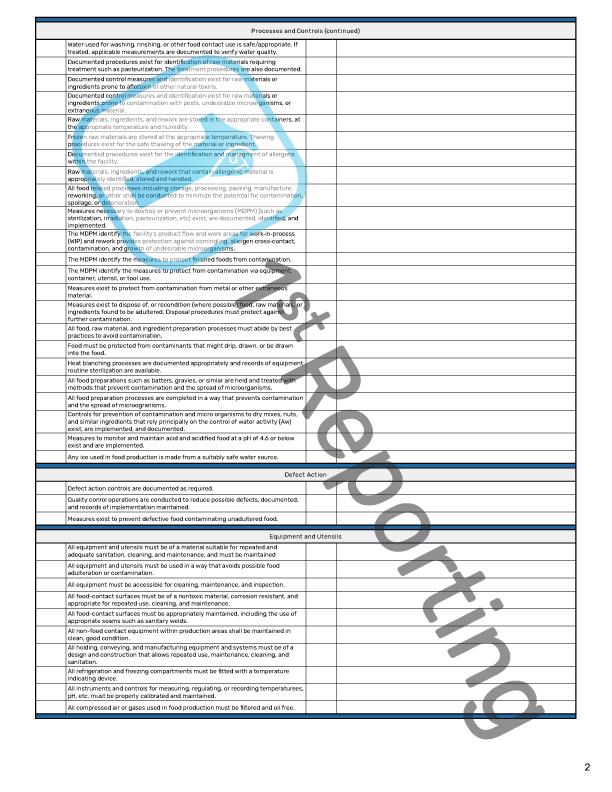


You’ll find our Food GMP Audit Checklist has four pages, subdivided into 15 sections. These sections comprise the bulk of a food industry GMP inspection and are as follows:
Administrative
Your auditor includes their name, date, facility information, and report number for document tracking.
Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory requirements begin our GMP audit checklist, ensuring your auditor starts with the proper mindset.
Food Safety Plan
Following regulatory requirements continues with the FSP inspection.
Personnel Qualifications and Training – Documentation is critical, and maintaining training records is equally essential. This section focuses on the proper GMP-related practices.
Personnel Hygiene
An essential aspect of a safe food production environment, the personnel hygiene section covers your team member best practices in production areas.
Supply Chain
The supply chain section deals with the GMP issues related to acquiring raw materials, ingredients, and goods.
Processes and Controls
No GMP audit is complete without an analysis of the GMP processes and controls established and maintained by the company.
Defect Action
Corrective actions and processes for defects and mitigating them.
Equipment and Utensils
Best GMP practices pertaining to the use of equipment and utensils in a food manufacturing environment.
Sanitary Facilities and Controls
Best GMP practices include measures to ensure sanitary facilities and control such.
Maintenance and Sanitation
Similar to the above section, the maintenance and sanitation section focuses on more facility-wide practices pertaining to the care and sanitation of the facilities.
Warehousing and Distribution
Food storage and transportation must also adhere to best GMP practices. This section includes the related checkpoints.
Food By-Products for Animal Food
If applicable to your operation, we’ve included the food by-product checkpoints when animal food product manufacturing is a part of your operations.
Facility and Grounds
The final portion of the food GMP audit is to inspect and note GMP practices about the facility and grounds.
Notes and Sign-Off
The final section of the 4-page Food GMP Audit Checklist pertains to any last notes not yet included in the report and a sign-off area for the auditor to validate the procedure.
How To Use The Food GMP Audit Checklist Effectively
To effectively utilize our Food GMP Audit Checklist, it is imperative that you have your staff appropriately trained on GMP best practices pertaining to your specific operational case.
According to a study by the FDA, the experts polled agreed that the four top GMP issues for food manufacturers are:
- Deficient team member training
- Contamination of raw materials
- Poor plant and equipment sanitation
- Poor plant design and construction.
Knowing these facts, we can consider a strategy for focusing on training and implementing the appropriate building construction and equipment for best GMP practices.
“Results from the study also indicated that refrigerated and dairy foods have the highest general risk of food safety problems compared to other food categories. Baked and refrigerated foods pose the highest risk in terms of allergen hazards. The expert elicitation also showed that the needs of small and medium-sized food processors likely vary from larger processors, with smaller facilities generating higher risk scores than large facilities across all food safety problems and sectors considered.”
FDA
Effective use of the Food GMP Audit Checklist means that your organization performs regular self-analysis and routine GMP self-audits. Why? Because it’s best that you catch GMP failures before there is a contamination issue or, worse – a potential health or safety hazard.
The four critical components to effective use of the GMP checklist within prevention and control measures include:
- Training – Routine training and refresher training in GMP best practices and the use of our checklists for internal audits ensure the best chances of success.
- Routine Audits – Routinely scheduling self-audits is vital to preventing contamination or other food manufacturing issues.
- Documentation – Documenting your GMP audits, practices, and procedures via printed reports, checklists, or, even better, via a digital application like 1st Reporting allows you to assess and analyze your findings. Documentation will enable you to provide proof of due diligence and also allows for audit tracking.
- Validation and Evaluation – Evaluation of training, GMP practices, the use of the GMP checklist, and even other templates used for various GMP processes is vital to the progressive evolution of your GMP practices.
In summary, use the checklist for routine, and regular GMP audits after thorough instruction to auditing staff. Analyze the audit results and act to mitigate any issues or concerns brought to light by the GMP audit checklist and documentation.
7 Tips For Easier And More Effective Food Industry GMP Audits
Use the following tips to train your auditing staff on GMP audit best practices. These tips will help to create a more efficient, effective, and professional GMP auditing process.
Plan Ahead:
Planning is key to an effective and efficient food industry GMP audit. Make sure you have a detailed plan of what you will be auditing and how you will be auditing it. It will help reduce the amount of time wasted on the audit.
Familiarize Yourself With The Facility:
Before starting the audit, ensure you are familiar with the facility and its processes. It will help ensure you do not miss any essential areas during the audit.
Be Thorough:
When conducting the audit, be sure to be thorough in your approach. Do not just glance over areas; take the time to scrutinize them.
Use Checklists:
Using checklists like our Food GMP Audit Checklist can help ensure you do not miss any essential steps during the audit. It also helps to ensure that all facility areas receive an adequate inspection.
Take Notes:
Taking notes during the audit is essential so that you can refer back to them later if needed. It will also help ensure that you inspect all facilities properly and thoroughly.
Pro Tip: Try using 1st Reporting to document your GMP audit. You can add media files like photos and videos to be more descriptive and concise in your report when you find issues.
Stay Organized:
Staying organized during an audit can help make it run more smoothly and efficiently. Ensure you have a system for tracking what you have audited and what still needs completion. For example, using our Food GMP Audit Checklist to follow audit steps and document findings is one effective means of tracking your inspection.
Follow-Up:
Following up after the audit is essential to ensure that responsible parties take the onus to complete all corrective actions and that the facility complies with GMP requirements. We recommend that if you require corrective actions, use a request template to ensure tracking of the proper corrective actions. Tracking allows for easier implementation management.