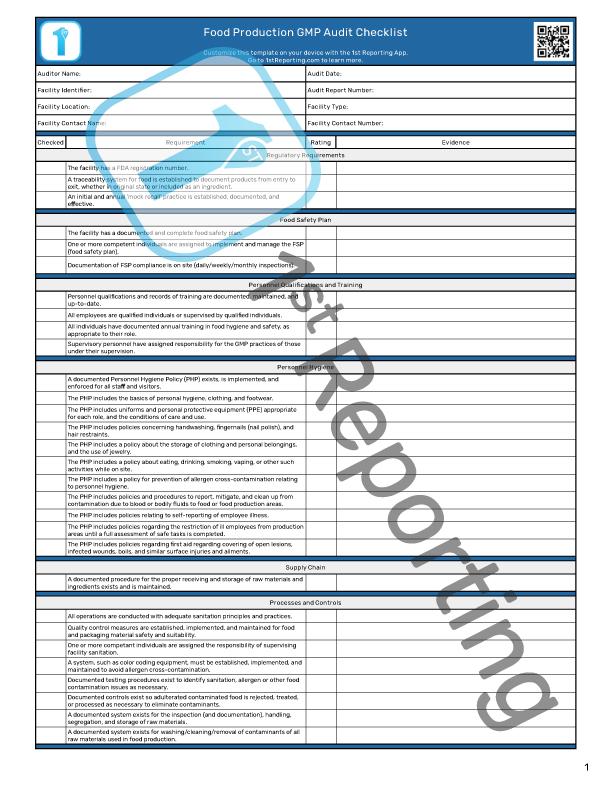
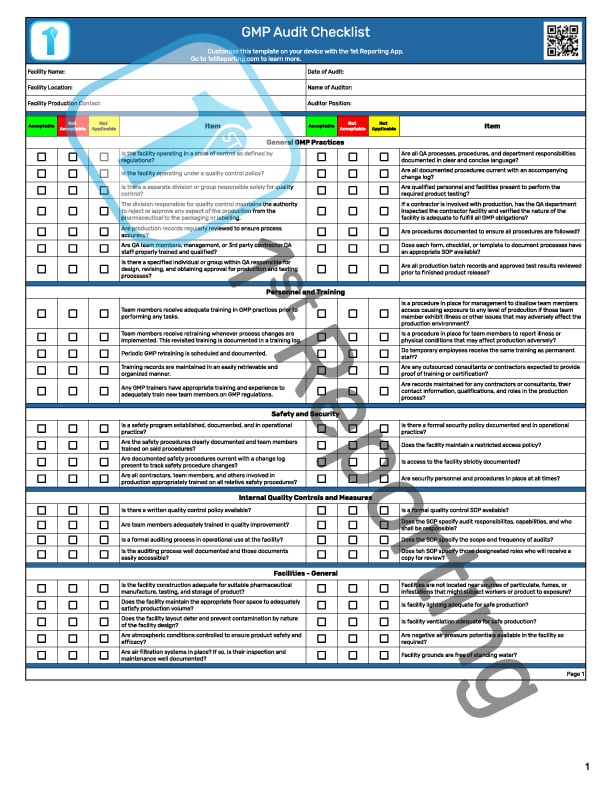
A clear and concise understanding of performing a GMP audit is vital for effective management. If you want to make the management process more straightforward, this guide is for you. You can use this guide to help train your team to perform fast, effective, and highly efficient audits using our templates or even more effectively using our app.
Performing a routine internal GMP audit is vital, but it can be a liability if you miss certain specific steps or checkpoints. Therefore, using a GMP audit checklist is the best way to ensure an effective audit.
Before you send your team out into the world using one of our downloadable templates, or for those seeking a higher level of efficiency and effective management using our app, you’ll need to provide your team performing the GMP audit with the appropriate training.
That’s where this guide comes in handy. Feel free to bookmark this page, and share it with your team to aid them in effectively learning the GMP auditing process.
What is a GMP Audit
A GMP audit is an inspection of a company’s good manufacturing processes. This type of audit is mandatory for specific industries, such as food, cosmetics, and drug production.
The Purpose of GMP Audits
GMP audits are essential because they help ensure that a company follows the best practices for making things that could cause harm if completed incorrectly. It helps keep people safe and can also help a company stay in compliance with the law.
There are two primary forms of GMP audit – the self-audit and the enforced audit.
Self-auditing is a wise practice we strongly recommend. You can use our templates like the Food GMP Audit Checklist or the GMP Audit Checklist we created to help the Pharmaceutical Industry. Or, if you prefer a much more robust solution, we have the 1st Reporting app – an application designed explicitly to manage audits and inspections easily.
Self-audits are essential to ensure that your organization remains compliant with regulations and GMP requirements without fear of retribution from regulators.
Enforced audits are those deemed necessary by a regulatory body. These audits can spark fear in the hearts of managers who are ill-prepared to face the inspection. However, a standard self-auditing methodology for compliance will ensure there is no fear but fear itself.
Speaking of performing self-audits, let’s look at how to achieve the best results.
How To Perform A GMP Audit In 8 Steps
We’ve analyzed the auditing process and determined that an eight-step process is necessary to ensure successful implementation.
- Define the scope of the audit
- Gather information about the company and its products
- Perform an on-site inspection
- Review documents and records
- Interview employees
- Assess GMP compliance
- Draft a report
- Follow up with management
That’s a vague list, so let’s ensure we’re on the same page and go into more detail.
Define the scope of the audit
The first step in any GMP audit is to define the scope of the inspection. It means deciding which areas of the company and what products will be included in the audit. It’s essential to be as specific as possible when defining the scope so that the inspector can conduct the audit effectively.
Gathering information about the company and its products
Once the scope has been defined, the next step is to collect information about the company and its products. You can do it by reviewing documents and records, interviewing employees, and conducting tests on products. This information will help inspectors understand the company’s operations and what GMP compliance issues may exist.
Performing an on-site inspection
The third step in a GMP audit is to perform an on-site inspection. It involves visiting the company’s facilities and observing how they operate. Inspectors will check for GMP compliance, safety measures, and product quality control.
The on-site inspection will require specific tools. Most notably, your auditor will need a means of documenting their findings. The traditional method is to use a GMP Audit Checklist.
However, suppose you’re a savvy manager who wants brownie points for adopting a more effective and efficient solution. In that case, you should consider trying 1st Reporting. It’s our app we designed to be the perfect solution to replace the dinosaur-like printed paper form.
Reviewing documents and records
After the on-site inspection, the next step is to review documents and records. It includes manufacturing procedures, quality control reports, and team member training manuals. Reviewing these documents can help inspectors better understand how the company operates and identify potential GMP compliance issues.
Wouldn’t it be great if all the inspection documents were easily accessible in one place? And wouldn’t it be great to access those documents from your mobile device, anywhere? It would be best if you considered using 1st Reporting for your inspections and audits. That way, you get extraordinary functionality like automated custom notifications and get all your documents from assessments in one place (and it isn’t an ugly filing cabinet). Try 1st Reporting today and see how it can easily help you retrieve your inspection documents for review.
Interviewing employees
The fifth step in a GMP audit is to interview employees. It helps inspectors understand how the company functions and learn about potential GMP compliance issues. Employees can also provide valuable insights into how the company operates and what improvements could be made.
It’s standard for self-auditing processes to skip or glaze over this stage. However, this audit stage is as crucial as any other and should not be overlooked.
Assessing GMP compliance
After gathering all this information, the next step is assessing GMP compliance. It involves evaluating how well the company follows good manufacturing practices and identifying areas that need improvement. Inspectors will also look at safety measures and product quality control processes to ensure they meet GMP standards.
Drafting a report
Once all this information has been gathered, it’s time to draft a report. This report will summarize everything learned during the GMP audit and provide recommendations for improving GMP compliance. It’s essential to be thorough when drafting this report to be used as a reference for future audits.
Follow up with management.
After the GMP audit is done, the inspector will write a report. This report will have all the information from the GMP audit. The inspector will then talk to management about the report and what needs to be done to improve GMP compliance.
GMP Auditor Qualifications

GMP auditors are people who inspect a company to see if they are following good manufacturing processes. It is essential because it helps ensure that essentials like food and medicine are made safely. GMP auditors need to know a lot about how to do this, and they also need to be able to follow up with management to make sure they are staying in compliance with the law.
GMP Documentation Requirements
GMP documentation requirements are the rules companies must follow when making products like food and medicine. They make sure that the products are made safely. GMP auditors check to see if companies are following these rules.
Not sure what information you might need to consider? Here’s a quick resource by country to help you find specific information:
Australia:
Code of good manufacturing practice for medicinal products
Canada:
United States:
GMP Regulations and Historical Preambles
Why GMP Self-Audits Are Critical To Operations

GMP audits are essential because they help companies follow good manufacturing processes. It is critical because it helps ensure that food and medicine are made safely. GMP audits also help identify areas where a company could improve its GMP compliance.
GMP Inspection Process – Internal or External Auditors?
When you do an internal GMP audit, someone from your company will look at how you make things and see if you are following the rules. If you have an external GMP auditor, they will come to your company to do the same thing, but they work for a different company.
The benefits of each should be obvious, but primarily the internal audit can allow preparations to occur before a government inspection without the risk of external party involvement or cost. The benefits of utilizing an external auditor are that they are impartial to your operations and will provide an unbiased report.
GMP Noncompliance and Corrective Actions
GMP noncompliance means not following the rules for making food and medicine. If a company does not follow these rules, it might have to take corrective actions. It could mean fixing the problems found during the GMP audit or doing something else to ensure the company follows GMP standards. In severe cases, a company might require issuing a recall.
8 Tips For Efficient GMP Audit Practices

Were you looking to improve your audit efficiency? We can help. Aside from our inspection app, 1st Reporting, we’ve got eight tips to help you streamline your auditing process.
- Plan your audits well and allow enough time for all necessary preparations.
- Make sure you understand entirely the GMP requirements that you will audit.
- Familiarize yourself with the company’s GMP history and any recent changes or updates to the GMP system.
- Prepare an audit plan and checklist explicitly tailored to your audit objectives.
- Conduct a preliminary walkthrough of the facility to get a general overview before starting the audit.
- Review GMP records and documents before meeting with management or personnel from affected areas/departments.
- Ask questions and probe beneath the surface during interviews rather than just accepting answers at face value.
- Utilize observations and documentary evidence to support findings during the closing meeting/report writing stage.
Take these eight steps into consideration when you develop your audit process methodology, and you’ll be well on your way to a more successful audit process. However, if you want to improve efficiency, learn more about the features of 1st Reporting that could exponentially improve your auditing times.
- Dynamic Incident Template Builder ts you create the exact form you need for your company.
- Robust Template Library – Take advantage of our pre-built templates to get started with a wide selection useful for multiple industries.
- Multimedia Tools – What can 1st do that a paper form can’t? Well, including photos, audio, or video is a great place to start.
- Automated Custom Notifications – Let the right person know when a specific event form gets completed by your team. With a custom automatic notification, you can ensure that the suitable supervisor is notified at the right time and for the right reason.
Need help figuring out integration? Not to worry, you can book a free demo with one of our specialists, who can walk you through getting things set up quickly.
Frequently Asked GMP Audit Questions
How often should I do an internal GMP audit?
The accepted standard frequency for internal GMP audits is a minimum of annually. They should increase their internal GMP audit frequency accordingly for complex or busy operations or operations involving materials prone to issues.
How many internal GMP auditors should a company have?
The number of internal GMP auditors trained at your facility will be directly related to the size of your operation. Similarly, it will also be affected by the complexity and frequency of your GMP audits and the amount of time and labor required for a successful audit.
It will be best to manage the audit labor time compared to the time necessary to shut down operations to facilitate a stop work order. So, always ensure you have enough internal auditors on staff to complete your internal audits effectively.
Do I have to report issues found in an internal GMP audit?
Issues discovered during an internal GMP audit should be addressed and communicated to the facilities management as soon as possible. Management will determine the nature of the issue discovered and its severity against operations. If there is a public risk, management will act accordingly to ensure the safety of the people and the product’s appropriate use.