GMP Vs. CGMP – Sometimes, the acronyms take over, don’t they? However, it’s best not to assume you know the answers when it’s something as essential as Good Manufacturing Practices.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, a series of regulations about the manufacture of goods for personal uses such as eating (food manufacturing), medicinal (pharmaceutical manufacturing), and cosmetic (cosmetics manufacturing).
cGMP stands for Current Good Manufacturing Practices. The conceptual difference between the two is that the “c” tells the manufacturer to use current technology practices and current regulatory standards.
Of course, we’re just scratching the surface here, so it’s best to dive deeper. After all, understanding the concepts behind the regulations and how they pertain to our businesses is critical.
GMP Vs. CGMP Deep Dive

GMP Regulations
Generally speaking, many manufacturing process regulations are pretty vague. The reason behind this is sound, as there are just too many types of manufacturing to cover all the best practices possible. Therefore, organizations like the FDA have committed to creating standard GMP regulations that remain flexible for use in multiple industry scenarios.
GMP Resources by Country
Government of Australia – Good manufacturing practice – an overview – This page of the Australian Government’s Department of Health and Aged Care website contains information about Australian GMP regulations.
Government of Canada – Guidance Documents – Good Manufacturing Practices – This page of the Canadian Government website links to all sorts of government publications about GMP regulations in Canada.
Government of the United States of America – Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) Regulations – This Food and Drug Administration page contains information about the latest CGMP regulations.
Government of the United Kingdom – Good manufacturing practices and good distribution practices – This page of the United Kingdom’s government website covers UK regulations regarding GMP.
Regulation Interpretation

One of the most challenging aspects of managing GMP and cGMP (or CGMP, depending on where you read it) is interpreting the regulations and how they directly pertain to your particular operation.
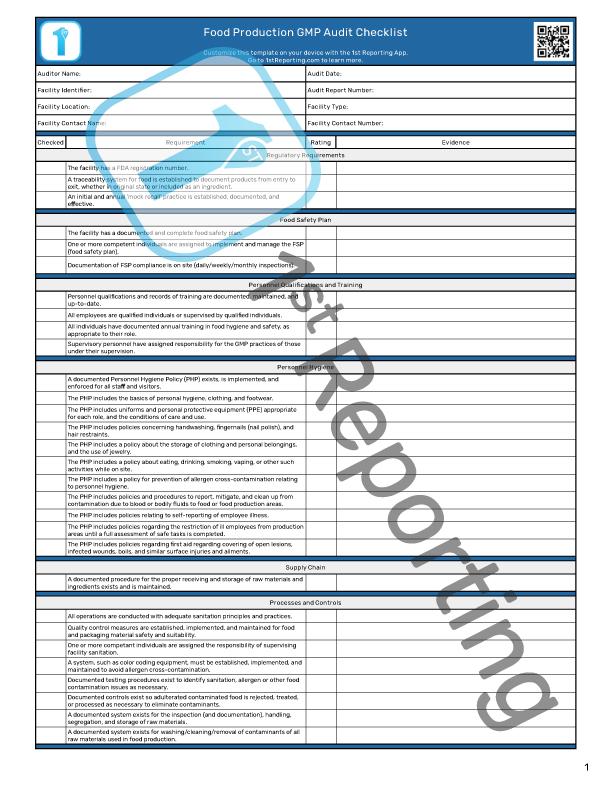
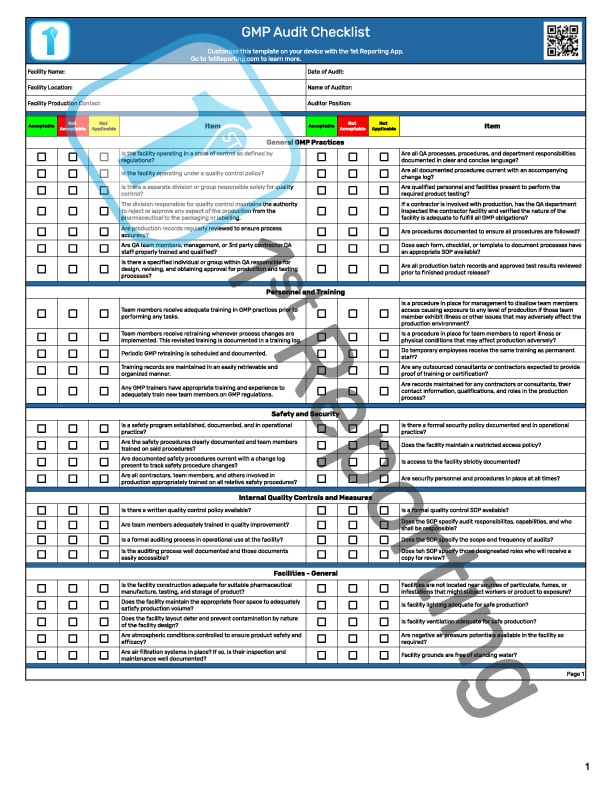
We’ve created several GMP audit checklists you can use, depending on your industry, to best complete your GMP inspections. However, you’ll still need to interpret the regulations and your choices for each stage of the manufacturing process. You’ll do this to ensure you are using current means of controlling and improving safety and product efficacy.
cGMP Concepts and Standards
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, the concept of cGMP is simple: consider using the most current methodology first, assuming it’s more innovative, with greater efficacy, and current.
That’s the “C” in cGMP.
But what about the other parts of the acronym? Here’s where things can start to get confusing:
G – The “G” in cGMP stands for “Good,” meaning that your manufacturing practices should be good (i.e., effective, efficient, and safe).
M – The “M” in cGMP stands for “Manufacturing.” So, your good manufacturing practices should extend to all aspects of the manufacturing process (e.g., materials, methods, facilities, controls).
P – The “P” in cGMP stands for “Processes.” So, your good manufacturing practices should ensure that all processes are carried out consistently and controlled.
Now that we know the meaning of cGMP let’s look at some of the standards that fall under this category.
Standards with cGMP Implications
There are a variety of standards that have cGMP implications. However, not all of them are created equal. Some, like ISO 9001, are widely recognized and used across industries. Others, like the FDA’s 21 CFR 820 (which covers medical devices), are more specific to particular products or businesses.
Below is a list of some of the more commonly used standards with cGMP implications:
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems – Requirements
- ISO 13485: Medical devices – Quality management systems – Requirements for regulatory purposes
- FDA 21 CFR 820: Quality system regulation for medical devices
- IEC 62304: Medical device software – Software life cycle processes
- ISO 14971: Application of risk management to medical devices
- ISO 25424:sterilization of medical devices – Requirements for manufacturers
While this is by no means an exhaustive list, it does cover some of the more commonly used standards.
Auditing for cGMP Compliance
In order to ensure compliance with cGMP regulations, auditing is a vital tool. Audits can be conducted internally (by company employees) or externally (by independent third-party organizations).
Internal audits are usually conducted annually and focused on ensuring that everyone follows the quality management system procedures. External audits, on the other hand, are typically conducted every two to three years and are more focused on whether or not the company is complying with cGMP regulations.
When conducting an audit, there are several things to consider:
- The auditor should have a good understanding of cGMP regulations.
- The auditor should be professional in the way they conduct the audit.
- The audit should be thorough and cover all aspects of the company’s operations.
- The auditor should be impartial and objective.
After the audit, the auditor will issue a report that includes their findings and recommendations. It is up to the company to decide whether or not to implement the recommendations.
Implementing GMP and cGMP Changes
Once you’ve determined what changes need implementation to comply with cGMP regulations, the next step is implementing those changes. It can be daunting, especially if you’re making significant changes to your manufacturing process.
In order to help make the transition smoother, you must create and set a plan in place. The plan should include the following:
- A timeline for implementing the changes.
- A list of who will be responsible for each task.
- A budget for the project.
- A method for tracking progress and measuring success.
Changing your manufacturing process can be challenging, but it’s essential to remember that the goal is to improve safety and product efficacy. By following the steps outlined above, you can ensure your transition goes as smoothly as possible.
Conducting Training
Once you implement the changes, training your employees on the new procedures is essential. It ensures that everyone on your team is on the same page and that the team follows the changes correctly.
When conducting training, there are several things to
consider:
- Ensure that someone knowledgeable about cGMP regulations
- performs the training. Trainers should possess a valid and recent accreditation or certification.
- You should tailor the training to the specific needs of your employees.
- The training should be interactive and engaging.
- You should conduct the training promptly.
Ensuring your employees are adequately trained on the new procedures is essential for compliance with cGMP regulations. By following the tips above, you can ensure that your employees are ready to implement the changes.
Maintaining GMP and cGMP Compliance.
Once you’ve made the changes and trained your employees, it’s essential to maintain compliance with cGMP regulations. It can be done by:
- Conducting regular audits.
- Making sure that employees are following the new procedures.
- Keeping up with changes in cGMP regulations.
Maintaining compliance with cGMP regulations is an ongoing process. Following the steps outlined above, you can ensure that your company stays compliant.
The Best Tool For GMP and cGMP Auditing: 1st Reporting
If you like improving efficiency, automating mundane tasks, and ensuring that GMP and cGMP requirements are met, then you’ll love the 1st Reporting app.
We’ve fine-tuned the app to work seamlessly with your team, whether working in-factory or in the field. Our inspection app will aid your auditors by:
- Increasing audit efficiency
- Decreasing auditor mistakes
- Increasing communication efficiency with automated and customizable notifications
- Allowing multimedia inclusion in the audit report
Our app has plenty of features that make it helpful for more than just GMP audits. The app works great for incident reporting, vehicle inspections, and even team member health declarations. Combine the robust management dashboard and a custom form builder that lets you make the precise forms and checklists to meet your exacting requirements, and you’ve got a winning tool in your tool belt.
Are you ready to improve your GMP and cGMP audits (and make your job easier)? Try the 1st Reporting app today. Start a free trial here, book a demo here, or download the app on Google Play or The Apple App Store.